
Written By : Getahun Teferi SAP Functional and Business Consultant Electrical and Computer Engineer Certified SAP Digital Badge in SAP S_4HANA Cloud - Support and Success Essentials for SAP Consultant
SAP Human Resource Management
Welcome to the free SAP HR Training Course created by volunteer authors. In this course, you will learn SAP HR (HCM) module from an absolute beginner to advanced level. SAP HCM and SAP HR are two names (new and old respectively) for the module of SAP ERP software that is responsible for human resources in companies. SAP HCM is considered to be one of the core modules of SAP ERP and our online course will help you to learn it.Our course consists of multiple tutorials organized in modules that you can see below. The course is completely self-paced, so you decide yourself when you start and finish learning. And, it delivers an excellent value for a free course.
Module 0: Introduction to SAP
Tutorial 0.1: What is SAP?
Tutorial 0.2: SAP for Beginners
Module 1: Getting Started with SAP HR
Tutorial 1.1: SAP HCM Overview
Tutorial 1.2: SAP HR Basics and Navigation
Tutorial 1.3: SAP HCM Organizational Structure
Module 2: Personnel Administration
Tutorial 2.1: SAP HCM Personnel Administration
Tutorial 2.2: Structures in SAP HR
Tutorial 2.3: SAP Personnel Structure
Tutorial 2.4: SAP HR Enterprise Structure
Tutorial 2.5: SAP HR Infotypes
Tutorial 2.6: SAP Infotype Screen Modification
Tutorial 2.7: SAP Infotype Menus
Tutorial 2.8: SAP Infotype Header Configuration
Tutorial 2.9: SAP Time Constraints
Tutorial 2.10: SAP HR Personnel Actions
Tutorial 2.11: SAP HCM Features
Tutorial 2.12: SAP Fast Entry
Tutorial 2.13: SAP Personnel Number Assignment
Tutorial 2.14: SAP Personnel Administration Reports
Tutorial 2.15: SAP Organizational Key
Tutorial 2.16: SAP Dynamic Actions
Tutorial 2.17: SAP Infotype Change Log
Module 3: Organizational Management
Tutorial 3.1: SAP Organizational Management Overview
Tutorial 3.2: SAP Organizational Management Structures
Tutorial 3.3: SAP HR Simple Maintenance in Expert Mode
Tutorial 3.4: SAP Infotype Maintenance in Expert Mode
Tutorial 3.5: SAP Organization and Staffing
Tutorial 3.6: SAP Organizational Management Actions
Tutorial 3.7: SAP Organizational Management Reports
Tutorial 3.8: SAP Organization and Staffing Configuration
Tutorial 3.9: SAP Evaluation Paths
Tutorial 3.10: SAP PPOME Transaction Configuration
Module 4: SAP Time Management
Tutorial 4.1: SAP Time Management Overview
Tutorial 4.2: SAP Planned Working Time Infotype
Tutorial 4.3: SAP Holiday Calendar
Tutorial 4.4: SAP Work Schedules and Their Elements
Tutorial 4.5: SAP Break Schedules Configuration
Tutorial 4.6: SAP Daily Work Schedule Configuration
Tutorial 4.7: SAP Period Work Schedule and Day Types
Tutorial 4.8: SAP Work Schedule Rules Configuration
Tutorial 4.9: SAP Time Management Infotypes
Tutorial 4.10: SAP Absence Quotas
Tutorial 4.11: SAP Time Constraint Class
Tutorial 4.12: SAP Absence Types Configuration
Tutorial 4.13: SAP Absence Counting Rule
Tutorial 4.14: SAP Absence Management
Tutorial 4.15: SAP Absence Rounding Rule
Tutorial 4.16: SAP Absence Quota Configuration
Tutorial 4.17: SAP Absence Quota Generation Rules
Tutorial 4.18: SAP RPTQTA00 Quota Generation Report
Tutorial 4.19: SAP Quota Deduction
Tutorial 4.20: SAP Time Management Reports
Module 5: Recruitment
Tutorial 5.1: SAP HR Recruitment Process
What is SAP?
What is SAP? Let’s get a clear understanding about what people can mean when using this word. The SAP acronym can mean two things:
1. SAP is a software system that integrates internal and external management information across an entire organization. It embraces finance, manufacturing, sales and service, CRM, etc. SAP automates these activities with an integrated software application. Purpose of SAP is to facilitate the flow of information between all business functions inside the boundaries of the organization and manage the connections to outside stakeholders.
2. SAP is a German company that actually developed this software system.
What is SAP? An ERP System
When people talk about SAP, they usually mean the software system called SAP ERP. SAP ERP consists of several parts, which are called “modules”. Some common modules, such as finance and accounting, are adopted by nearly all users of SAP. Others such as human resource management are not. For example, a service company probably has no need for a manufacturing module. Other companies already have a system that they believe to be adequate. Generally speaking, the greater the number of modules selected, the greater the integration benefits, but also the greater the costs, risks and changes involved. There are following modules:
- Finance/Accounting (FI). It helps to manage accounting operations of a company (General ledger, payables, cash management, fixed assets, receivables, budgeting, consolidation).
- Human resources (HR). It helps to manage human resources of a company (Payroll, training, benefits, 401K, recruiting, diversity management).
- Manufacturing (PP). It helps to manage manufacturing processes of a company (Engineering, bill of materials, work orders, scheduling, capacity, workflow management, quality control, cost management, manufacturing process, manufacturing projects, manufacturing flow, activity based costing, product life cycle management).
- Supply chain management (SCM). It helps to manage logistics processes of a company (Order to cash, inventory, order entry, purchasing, product configuration, supply chain planning, supplier scheduling, inspection of goods, claim processing, commissions).
- Project management (PM). It helps to manage projects within a company (Costing, billing, time and expense, performance units, activity management).
- Customer relationship management (CRM). It helps to manage relations with customers of a company (Sales and marketing, commissions, service, customer contact, call center support).
- Data services. Various “self–service” interfaces for customers, suppliers and/or employees.
- Access control. Management of user privileges for various processes.
SAP scope usually implies significant changes to staff work processes and practices. Generally, three types of services are available to help implement such changes — consulting, customization, and support. Implementation time depends on business size, number of modules, customization, the scope of process changes, and the readiness of the customer to take ownership for the project. The typical project for a large enterprise consumes about 14 months and requires around 150 consultants. Small projects can require months; multinational and other large implementations can take years. Customization can substantially increase implementation times.The fundamental advantage of SAP is that integrating the myriad processes by which businesses operate saves time and expense. Decisions can be made more quickly and with fewer errors. Data becomes visible across the organization. Tasks that benefit from this integration include:
- Sales forecasting, which allows inventory optimization
- Order tracking, from acceptance through fulfillment
- Revenue tracking, from invoice through cash receipt
- Matching purchase orders (what was ordered), inventory receipts (what arrived), and costing (what the vendor invoiced)
SAP centralizes business data, bringing the following benefits:
- It eliminates the need to synchronize changes between multiple systems—consolidation of finance, marketing and sales, human resource, and manufacturing applications
- It enables standard product naming/coding.
- It provides a comprehensive enterprise view (no “islands of information”). They make real–time information available to management anywhere, any time to make proper decisions.
- It protects sensitive data by consolidating multiple security systems into a single structure.
I hope that you have a better understanding of what is SAP and why people use it. If you have any questions, let me know in the comments .
Target Audience of this Article
- Fresh Graduates willing to pursue their career in ERP or Software Designing or Solution Architecture
- Experienced Professionals who are working, very much in the field and gurus of their current line of business and are willing to pursue career in ERP design and implementation
- Experienced Professionals who have come across SAP during their professional career as either as a Power User or End User or Project Coordinator and want to pursue their careers in ERP design and implementation
- Experienced Professionals who are currently involved in developing business software and are willing to switch to an ERP design and implementation
- Experienced Professionals willing to make a drastic career switch from current career to ERP designing and implementation
Foreword
Before I entered in the SAP Consultancy, I had many questions. Mind was boggling with endless questions on how to proceed and become an SAP Consultant myself. All I knew was, that some SAP named product is there outside and its experts are very much high in demand plus this field pays very well with numerous opportunities to travel.
I am Completed SAP S/4HANA Cloud - Support and Success Essentials for SAP Cloud Solutions SAP Implementation and I got Certified Digital Badge since July 29,2022. SAP is one of the most broadly used SAP modules. SAP module covers SAP Finance and Controlling configuration, SAP HR configuration, SAP MM user and SAP SD user. Taking up an SAP certification is the first step towards establishing a career as an SAP consultant.
Module 1: Getting Started with SAP HR
SAP HCM Overview
Welcome to this familiarization tutorial on SAP Human Capital Management (HCM). The objective of this tutorial is to provide SAP HCM overview and discuss its components.SAP HCM is a comprehensive business solution to automate, streamline and optimize the various HR processes of a company, from recruit to retire. While HCM consists of many seamlessly integrated sub-modules, this tutorial will focus on some of the predominant ones as listed below.
Recruitment
The first component that we are going to discuss in SAP HCM overview is Recruitment. This component facilitates the end-to-end recruitment process of a company.
Key Features
- You can manage vacancies and advertisements, and assign vacancies to advertisements.
- Applicant administration enables the storage of all applicant data and classification of applicants.
- You can create letters for applicant correspondence, such as interview invites and offer letters.
- Selection of applicants is facilitated using applicant actions, such as “Invite applicant” or “Issue offer letter”.
- If an applicant is selected and you decide to hire him/her, the applicant data can be transferred to Personnel Administration. This eliminates the duplication of data entry effort.
- Various reports are provided to generate statistical data and lists on advertisements, vacancies and applicants.
Personnel Administration
Personnel administration is often considered the backbone of the SAP HCM module. And rightfully so. It is in this space that employees are hired, all their information is stored and their employment life cycle is recorded.
Key Features
- All employee data is stored in infotypes. Infotypes are logical groupings of related data fields. For example, an employee’s name, surname, birth date, marital status and religion are stored in the Personal Data infotype.
- Changes made to infotype data can be logged and subsequently analysed. You can control, via customizing, which infotypes and fields should be logged.
- Personnel actions are used to record personnel procedures like hiring, transfer, promotion and separation.
- HR authorizations ensure that all infotype data is secure and accessible to authorized users only.
- Several standard reports are provided to efficiently extract and evaluate HR data. If these do not meet the reporting needs of your company, ad hoc queries or customized reports can be developed.
Organizational Management
As we continue SAP HCM overview, let’s talk about organizational management for human resources in SAP ERP. This component is the basis for various business and HR processes, as well as for workflows. It is here where the organizational plan (a functional structure of an organization) is created and managed. The below picture shows an illustrative example of an organizational structure.
Key Features
- Organizational management is designed around the concept of objects, and relationships between the objects. There are numerous objects, the most important ones being Organizational Unit, Position, Job, Person and Cost Center.
- Objects are linked to each other via relationships. These relationships give rise to structures. For example, the relationships among organizational units (business units, departments, groups or teams) result in the organizational structure. The relationships between positions (e.g. the Assistant Manager position “Reports to” the Manager position) result in the reporting structure.
- These structures are of prime importance for the implementation of workflows.
- SAP provides various interfaces to efficiently create and edit objects, relationships and structures. Each of these interfaces will be covered in detail in the SAP HCM Organizational Management tutorial.
- Numerous reports are provided to efficiently extract and evaluate organizational data.
Time Management
Time management is the SAP HCM component that facilitates the planning, recording and valuation of employees’ working times.
Key Features
- Work schedules are used to indicate an employee’s planned working time, daily working hours, weekly work pattern and weekly days off. The below picture is an example of a work schedule:
- Public holidays can be created and assigned to holiday calendars.
- Employee time data can be recorded by employees themselves or by time administrators, supervisors or secretaries.
- Quota generation can be used to calculate leave entitlement in accordance with your company’s leave quota policy.
- There are two types of time management:
- Positive Time Management – All actual times must be recorded. This implies that, for any day, an employee will be considered absent unless a clock-in and clock-out action is recorded for that day. Attendance may also be manually entered by a manager.
- Negative Time Management – Only deviations from the work schedule must be recorded. In this case, for any day, an employee will be considered present unless an absence is explicitly recorded for that day.
- Time Evaluation is an optional sub-component which can be used to evaluate employees’ working times.
- Time Management can be integrated with Payroll. The payroll driver reads the inputs from time management, for example, to compensate overtime hours or to calculate loss of pay.
Payroll
SAP provides a robust payroll solution to calculate gross earnings, deductions and net pay in accordance with legal as well as company-specific policies.
Key Features
- Statutory regulations of every country are incorporated in country-specific payroll drivers provided by SAP.
- Company-specific payroll policies can be implemented through customizing and with the help of personnel calculation rules.
- Payroll inputs are read from payroll-relevant infotypes. These are then processed by the payroll driver, various calculations are performed and the payroll results are written to cluster tables.
- Payslips, company-specific reports as well as statutory reports can be generated.
- In addition to regular payroll carried out at fixed intervals, payroll can be executed as needed using off-cycle payroll.
- The payroll results can be posted to Accounting.
SAP HR Basics and Navigation
Welcome to the tutorial about SAP HR basics and navigation in SAP HR module. After completing this tutorial you will get initial understanding about working with Personnel Administration and Organization Management submodules of SAP HCM.
The purpose of this SAP HR tutorial is to describe in details the basics and navigation is SAP HR module. And mainly, in HR core submodules – Personnel Administration and Organizational Management. The rests of SAP HR submodules follow similar navigation rules.Let us start with a quick reminder of the SAP navigation features. On the image below you can see SAP logon screen and its main parts.
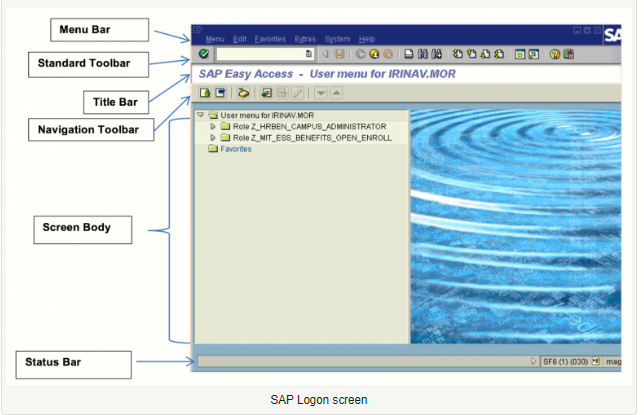
The Command Field in the top left corner stores and displays past transaction codes that have been entered.
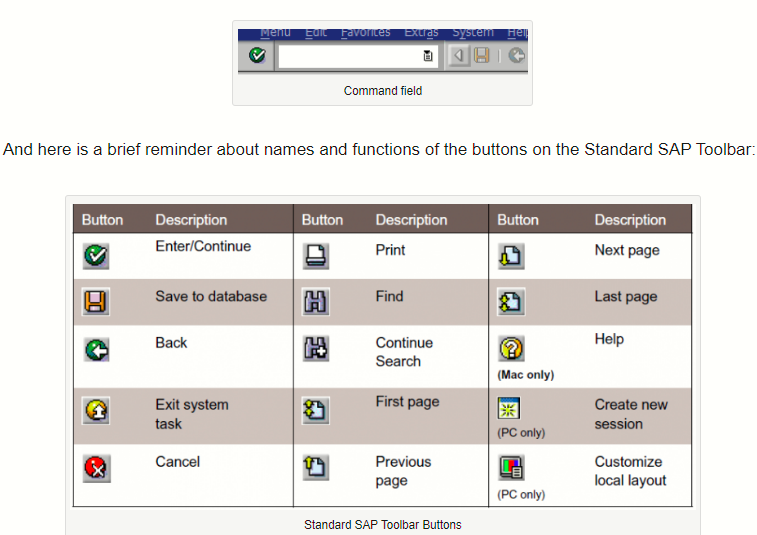
And here is a brief reminder about names and functions of the buttons on the Standard SAP Toolbar:
The status bar is the place where additional information about user, transaction, program and so on can be viewed.
SAP HCM Organizational Structure
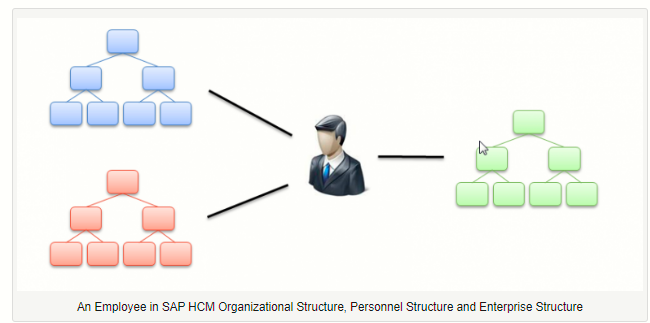
Welcome to the tutorial about SAP HCM Organizational Structure. After completing this tutorial you will get initial understanding about maintaining an organizational structure of an enterprise in the Organization Management submodule of SAP HCM.There are 3 fundamental structures in SAP HCM:
- Enterprise structure
- Personnel structure
- Organizational structure
Enterprise and Personnel structures are part of the Personnel Management and Organization structure is part of Organizational Management (OM) submodule of SAP HCM.The assignment to those 3 structures must allow to precisely locate any employee in the organization. Those structures are used to:
- Group together employees who share common rules and policies in terms of personnel administration, time management or payroll
- Generate default values
- Provide structures selection criteria
- Structure authorizations on master data
Overview of SAP HCM Organizational Structure
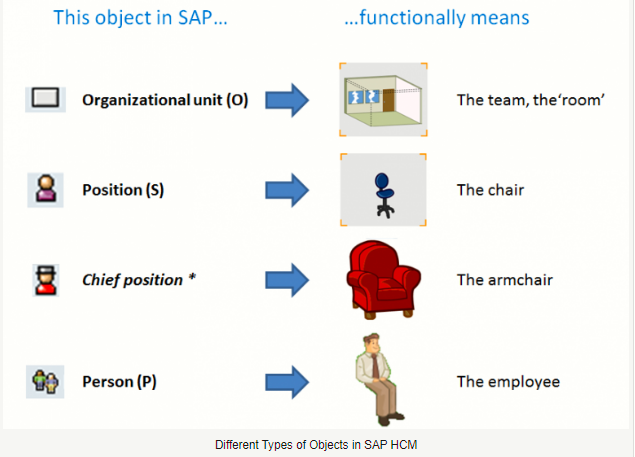
Now, let’s discuss SAP HCM organizational structure in more details. The organizational unit is a box in the pyramid of the organizational chart: a business unit, a department, a team, etc.
The position can be seen as a chair, on which will seat an employee, or a person.Those objects are far from being the only ones existing in Organizational Management (OM) and will be detailed later on in this presentation.
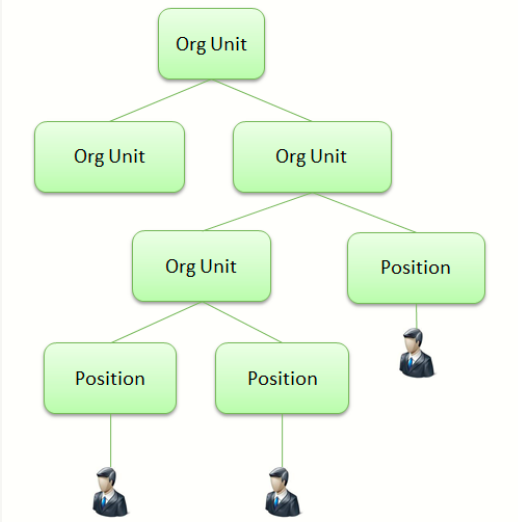
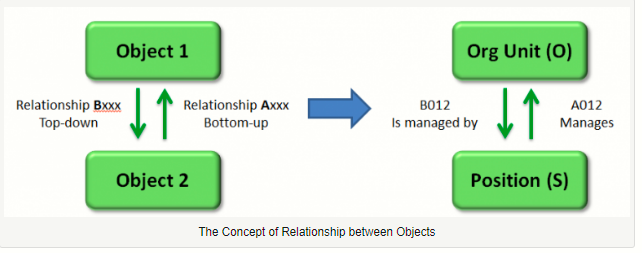
Objects and Relationships
OM uses the concept of object and relationship. The following rules apply:
- An object has a type and is useless if not linked to at least one another object
- A relationship is always both ways (A and B relationships)
- A relationship has a type, which has a functional meaning (for example, 008, 012, etc.)
- All relationships are not allowed between two defined object types
Example Text



