
Written By : Getahun Teferi SAP Functional and Business Consultant Electrical and Computer Engineer Certified SAP Digital Badge in SAP S_4HANA Cloud - Support and Success Essentials for SAP Consultant
SAP FI Business Processes
FI focuses on General Ledger Accounting and the processing of receivables (FI-AR), payables (FI-AP), and Asset Accounting (FI-AA). Important tasks of FI include the recording of monetary and value flows as well as the evaluation of the inventories.
Module 1: Getting Started with SAP FI
Tutorial 1.1: SAP FI Organizational Structure
Tutorial 1.2: How to create a company code in SAP
Tutorial 1.3: What is the Variant Principle in SAP FI?
Tutorial 1.4: SAP Fiscal Year and Fiscal Year Variants
Tutorial 1.5: Currencies in SAP
Tutorial 1.6: SAP Exchange Rates
Tutorial 1.7: SAP Exchange Rate Table
Tutorial 1.8: SAP Chart of Accounts
Tutorial 1.9: SAP G/L Account Segments
Tutorial 1.10: SAP Balance Sheet and P&L Statement Accounts
Tutorial 1.11: SAP Account Group of G/L Accounts
Tutorial 1.12: SAP Field Status Variant
Module 2: SAP FI Master Data
Tutorial 2.1: SAP General Ledger Account (G/L Account)
Tutorial 2.2: SAP Customer Account
Tutorial 2.3: SAP Vendor Account
Tutorial 2.4: SAP Bank Master Data
Module 3: SAP FI Documents
Tutorial 3.1: SAP FI Document Types
Tutorial 3.2: SAP FI Document Structure
Tutorial 3.3: SAP FI Posting Periods
Tutorial 3.4: SAP FI Posting Authorization
Tutorial 3.5: SAP FB50 Transaction Tutorial
Tutorial 3.6: SAP FI Tax
Tutorial 3.7: SAP Tax Configuration
Tutorial 3.8: SAP Document Change Rules
Tutorial 3.9: SAP Document Reversal
Module 4: Clearing Processes in SAP FI
Tutorial 4.1: SAP Clearing of Open Items
Tutorial 4.2: SAP Incoming Payment
Tutorial 4.3: SAP Outgoing Payment
Tutorial 4.4: SAP Tolerance Groups
Tutorial 4.5: SAP Payment Differences Processing
Tutorial 4.6: SAP Partial and Residual Payments
Tutorial 4.7: SAP Exchange Rate Differences
Module 5: SAP Cash Journal
Tutorial 5.1: SAP Cash Journal Configuration
Tutorial 5.2: SAP FBCJ Cash Journal
Module 6: Special G/L Transactions
Tutorial 6.1: SAP Special G/L Introduction
Tutorial 6.2: SAP Customer Down Payment Process
Tutorial 6.3: SAP Vendor Down Payment Process
Tutorial 6.4: SAP Bill of Exchange
Tutorial 6.5: SAP Posting Key Configuration
Tutorial 6.6: SAP Special G/L Indicator Configuration
Tutorial 6.7: SAP Statistical Entry Configuration
Module 7: Parking and Holding Documents in SAP
Tutorial 7.1: SAP Parking and Holding Documents
Tutorial 7.2: Post Parked SAP Documents
Tutorial 7.3: Post Parked Documents Using SAP Workflow
Module 8: Automatic Payment Program
Tutorial 8.1: SAP Payment Run Process
Tutorial 8.2: SAP Payment Program Configuration
Tutorial 8.3: SAP Payment Run Step by Step Demonstration
Tutorial 8.4: SAP Payment Medium Workbench
Tutorial 8.5: SAP Debit Balance Check
Module 9: Dunning
Tutorial 9.1: SAP Dunning Process
Tutorial 9.2: SAP Dunning Configuration
Tutorial 9.3: SAP Dunning Run Step by Step Demonstration
Tutorial 9.4: SAP Dunning Proposal Modification
Tutorial 9.5: SAP Dunning Notice
Module 10: Closing Activities
Tutorial 10.1: SAP Month End Closing Process
Tutorial 10.2: SAP Year End Closing Process
Module 11: Financial Statements in SAP
Tutorial 11.1: SAP Financial Statement Version
Tutorial 11.2: SAP Drilldown Reporting
Module 12: Accounts Receivables and Accounts Payables
Tutorial 12.1: SAP Balance Confirmation
Tutorial 12.2: SAP Foreign Currency Valuation
Tutorial 12.3: SAP Value Adjustments
Tutorial 12.4: SAP Regrouping Receivables Payables
Module 13: Accruals and Deferrals
Tutorial 13.1: SAP Accrual Deferral Posting
Module 14: Integration with Other Modules
Tutorial 14.1: SAP MM FI Integration
Miscellaneous
SAP Leased Assets Configuration Steps
SAP S/4 HANA FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
INTRODUCTION:
Business Processes in Financial Accounting in SAP S/4 HANA. You will post how SAP S/4HANA covers the Financial Accounting related business requirements and how the fundamental business processes and tasks are executed in the system. General Ledger Accounting, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Asset Accounting and Bank Accounting and their integration.
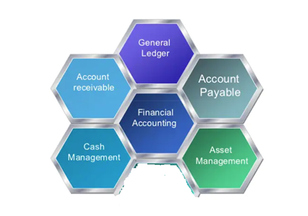
There are Five SAP FI Sub Module
1. General Ledger
2. Account Payable
3. Account and Receivable
4. Asset Account
5. Bank Account
SAP FI SUB MODULE OVERVIEW IMAGE
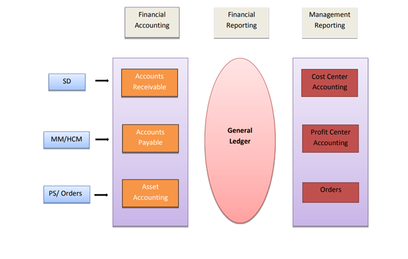
FICO FUNCTIONAL INTEGRATION WITH OTHER MODULE
SAP End Users:
SAP End Users are responsible for operating day-to-day transactions after the SAP project Go Live. In the case of Finance, an SAP FICO End User does activities like posting an invoice, collections, Purchase orders, Goods receipts, etc. What does an SAP FICO End User do daily? Users’ responsibilities are different as per different SAP modules.
Financial Accounting module:
Which deals in processing, recording, and maintaining financial accounting transactions within enterprises. It manages data involved in any financial and business transactions in a unified system and the module functions satisfy external reporting too. The Process and Business Transaction as follows:
1.General Ledger Accounting
Business Process Overview
General Ledger Accounting provides a comprehensive picture of accounting for external reporting Purposes. Recording all business transactions in the General Ledger ensures complete and accurate accounting data. It supports preparation of financial statements in custom defined formats.
Key processes in General Ledger
- Accounting Posting a general ledger document
- Display of document
- Display GL balances
- Display/Change GL Line items
- Carrying out recurring entries
- Clearing of GL open items – Automatic and Manual
- Year-End and Month-End closing activities
2. Account Payable:
Business Process Overview
Vendor Grouping & Master Data Maintenance – Creating Vendor Account Groups and Vendor Master Data Posting & Processing of Transactions - Invoices / Debit Memos / Outgoing Payments
- Invoice/Debit Memo posting either directly in FI (Financial Accounting) (without Purchase
- Order) or through integration with Materials Management.
- Logistics Invoice Verification - for the goods or services received, vendor invoice is posted and
- Automatic account postings are generated for the vendor liability and price difference, if any.
- Posting of payments to vendors against open items.
Down Payment Requests, Down Payments and Down Payment Clearing
- Manual down payment request and down payment can be made with or without purchase order reference.
- Down payment condition can also be maintained in the purchase order and down payment request in this case can be generated by the purchase department. The finance department would use the down payment request for making the down payment.
- Down payment can be cleared while posting an invoice.
Real-time integration with General Ledger – Transactions posted to a vendor account would automatically be posted to the Reconciliation GL account maintained in the vendor master.
3. Account Receivable:
Accounts Receivable is a submodule of SAP FI used to manage and record accounting data for all the customers. It handles customer invoices, approvals, payments and other allied activities. Any postings made in Accounts Receivable is updated in General Ledger G/L as well.
4.Asset Accounting:
Business Process Overview
4.1. Asset Acquisition:
Fixed Assets are either acquired externally or are internally built, made or manufactured.
4.1.1. External Acquisition Readily usable fixed assets like vehicles, computer hardware, furniture & fixtures, so on are acquired externally and are put to use immediately. The date of acquisition and capitalization would be the same in most of the cases.
4.1.2. Capitalization through Asset Under Construction (AUC):
In this case the fixed assets are not acquired externally but are made, built or manufactured in-house.
4.2. Transfer of a fixed asset within company code:
The location of an asset is identified with the Cost Centre maintained in the fixed asset master data. When there is a transfer of an asset from one department to another within the company or organization, the same can be recorded in the asset management module.
4.3. Sale of a fixed asset:
The sale of a fixed asset is accounted through a standard SAP transaction code. The system automatically calculates the depreciation for the fixed asset till the value date of the sale transaction and computes the gain or loss on the sale of the asset. The account postings are generated automatically due to the integration of Asset Accounting General Ledger.
4.4. Scrapping of a fixed asset
If an asset cannot be put to use and has to be scrapped, the process can be addressed through a standard SAP transaction
4.5. Depreciation posting
Depreciation is posted for the fixed assets periodically as per the policy of the company. The depreciation run can be executed monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annual in the SAP system.
4.6. Impairment of fixed assets
As per IFRS (IAS 16), at the end of each reporting period i.e., at the end of each fiscal year, the organization has to assess if any fixed assets qualify for impairment
5.Bank Accounting:
Business Process Overview
5.1. BANKS Accounts:
Organizations open accounts with banks for safe parking of funds and to do transactions of incoming and outgoing payments with vendors, customers, Government and other external agencies/parties, payment of salaries to employees, advances to employees, etc.
In some countries, payment transactions are required by law to be carried out only through banking channels so that a trail of the transactions is available. Cash transactions beyond a certain threshold limit is not allowed by law in some countries.
5.2. Payment Methods
The payment method is the medium by which payments are made, e.g., Cheque, bank transfer, etc. Organizations make payments by issue of cheques, advice for bank transfers and any other methods that are allowed and/or practiced in the country in which the organization is carrying out its business activities.
5.3. Bank Reconciliation
Reconciliation of the transactions carried out through banking channels are done periodically, i.e. daily, weekly or monthly as per the practice in the organization. The reconciliation is done between the transactions reflected in the bank statement and the transactions recorded in the books of account.
The bank reconciliation processes would facilitate the identification of transactions which are posted in the books of accounts but not appearing in the bank statement. For example, cheques issued to vendors but not presented for payment by the vendors. The bank reconciliation process also helps in identifying transactions like direct deposits in the bank account, debit of bank charges by the bank, etc.
SAP FI SUB MODULE PROCESS AND TRANSACTION
I. General Ledger
General Ledger Process:
No | General Ledger Process |
| 1 | GL Account Master Data |
| 2 | G/L Account Invoice Processing |
| 3 | Parking GL Documents |
| 4 | Display GL balances |
| 5 | Display/Change GL Line items |
| 6 | Carrying out recurring entries |
| 7 | Clearing of GL open items – Automatic and Manual |
| 8 | Year-End and Month-End closing activities |
| 9 | GL Account Reports |
General Ledger Transaction:
| No | General Ledger Transactions | T Code |
| 1 | GL Master Data | |
| 1.1 | Create Master GL | FS00 |
| 1.2 | Change Master GL | FS00 |
| 1.3 | Display Master GL | FS00 |
| 2 | Post G/L Invoice | |
| 2.1 | G/L Account Posting | FB50 |
| 2.2 | General G/L Account Posting | F-02 |
| 3 | Park G/L Account | |
| 3.1 | Post Park G/L Account | FV50 |
| 3.2 | Post Park G/L Account Genral | F-65 |
| 3.3 | Display Parked Documents | FBV3 |
| 3.4 | Change Parked Documents | FBV2 |
| 3.5 | Post Document Posting | FBV0 |
| 4 | GL Period End Closing | |
| 4.1 | Post Rent Account | F-02 |
| 4.2 | Create Recurring Entry Document | FBD1 |
| 4.3 | Change Recurring Document | FBD2 |
| 4.4 | Display Recurring Document | FBD3 |
| 4.5 | Display Change in Recurring Document | FBD4 |
| 4.6 | Delete Recurring Document | F.56 |
| 4.7 | Create Posting from Recurring Documents | F.14 |
| 4.8 | Running Batch Input Session | SM35 |
| 4.9 | Recurring documents list | F.15 |
| 4.10 | Enter Accrual/Deferral Document | FBS1 |
| 4.11 | Reverse Accrual/Deferral Document | F.81 |
| 5 | GL Account Display | |
| 5.1 | GL Line Item Display | FBL3N |
| 5.3 | GL Document Display | FB03 |
| 6 | GL Reports | |
| 6.1 | GL Account Balance | FS10N |
| 6.2 | GL Account Balance Display Single/Multiple GL | FAGLB03 |
| 6.3 | Trial Balance | F.08 |
| 6.4 | Execute Financial Statement | F.01 |
2. Account Payable:
Account Payable Process:
No | Account Payable Process | ||
| 1 | Vendor Master Data | ||
| 2 | Vendor Invoice Processing | ||
| 3 | Vendor Credit Management | ||
| 4 | Vendor Parking Documents | ||
| 5 | Vendor Outgoing Payment | ||
| 6 | Vendor Down Payment Process | ||
| 7 | Clear Vendor Account | ||
| 8 | Document Reversal | ||
| 9 | Reset Cleared Items | ||
| 10 | Display AP Line items | ||
| 11 | Display AP Balances | ||
| 12 | Various standard SAP AP reports |
Account Payable Transaction:
| No | Account Payable Transactions | T Code |
| 1 | Vendor Master Data | |
| 1.1 | Create Vendor Master | FK01 |
| 1.2 | Change Vendor Master | FK02 |
| 1.3 | Display Vendor Master | FK03 |
| 2 | Vendor Invoice | |
| 2.1 | Post Vendor Invoice | FB60 |
| 2.2 | Post Vendor Invoice General | F-43 |
| 3 | Vendor Credit Memo | |
| 3.1 | Post Vendor Credit Memo | FB65 |
| 4 | Vendor Park Document | |
| 4.1 | Park/Edit Credit Memo | FV65 |
| 4.2 | Park Vendor Invoice | FV60 |
| 4.3 | Change Parked document | FBV2 |
| 4.4 | Display Parked Document | FBV3 |
| 4.5 | Reject a Parked document – | FBV6 |
| 4.6 | Display Changes – Parked document | FBV5 |
| 4.7 | Post Parked Document | FBV0 |
| 5 | Post Outgoing Payment | |
| 5.1 | Post Standared Vendor Payment | F-53 |
| 5.2 | Post Vendor Partial Payments | F-53 |
| 5.3 | Post Vendor Resedual Payment | F-53 |
| 5.4 | Post Vendor "Automatic choose Invoice" Payment | F-53 |
| 5.5 | Post Vendor Manual Cheque Payment | F-53 |
| 5.6 | Payment with Printout Header Data | FBZA |
| 6 | Vendor Advance Payments | |
| 6.1 | Down Payment Request | F-47 |
| 6.2 | Post Vendor down payment | F-48 |
| 6.3 | Clear Vendor down payment | F-54 |
| 6.4 | List Of Down Payments Open | S_ALR_87012105 |
| 7 | Vendor Document Reversal | |
| 7.1 | Individual Document Reversal | FB08 |
| 7.2 | Mass Document Reversal | F.80 |
| 7.3 | Reset Cleared items | FBRA |
| 8 | Vendor Open Item Clearing | |
| 8.1 | Post Transfer with Clearing | F-51 |
| 8.2 | Manual Clearing | F-44 |
| 8.3 | Automatic Clearing | F.13 |
| 9 | Vendor Account Display | |
| 9.1 | Display Vendor Balance | FK10N |
| 9.2 | Vendor Line Item Display | FBL1N |
| 9.3 | Display Accounting document | FB03 |
| 10 | Vendor Account Report |
3. Account Receivable:
Account Receivable Process:
| No | Account Receivable Process |
| 1 | Customer Master Data |
| 2 | Customer Invoice Processing |
| 3 | Customer Credit Memo Processing |
| 4 | Park Customer Invoice Processing |
| 5 | Incoming Payments |
| 6 | Down Payment Process |
| 7 | Document Reversal |
| 8 | Clear Customer Account |
| 9 | Reset Cleared Items |
| 10 | Display AR Line items |
| 11 | Various standard SAP AR reports |
Account Receivable Transaction:
| No | Accounting Receivable Transactions | T Code |
| 1 | Customer Invoice | |
| 1.1 | Customer Invoice Posting | FB70 |
| 1.2 | Customer Invoice General Posting | F-22 |
| 1.3 | Customer Credit Memo Posting | FB75 |
| 1.4 | Customer Credit Memo General Posting | F-27 |
| 1.5 | Park Customer Invoice | FV70 |
| 1.6 | Park Customer Invoice General | F-64 |
| 1.7 | Change parked document | FBV2 |
| 1.8 | Change header parked document | FBV4 |
| 1.9 | Display change parked documents | FBV5 |
| 1.1 | Post Parked Customer Document | FBV0 |
| 2 | Post Incoming Payment | |
| 2.1 | Standared Incoming Payments (Total Balance & Document No.) | F-28 |
| 2.2 | Partial Incoming Payments (Total Balance & Document No.) | F-28 |
| 2.3 | Reseidual Incoming Payments | F-28 |
| 2.4 | Incoming Payment "Automatic choose Invoice" | F-28 |
| 3 | Cusomer Down Payment | |
| 3.1 | Customer Down Payment Request | F-37 |
| 3.2 | Post Customer Down Payment | F-29 |
| 3.3 | Clear Customer Down Payment | F-39 |
| 5 | Cusomer Open Item Clearing | |
| 5.1 | Manual Clearing | F-32 |
| 5.2 | Post with Clearing | F-30 |
| 5.3 | Automatic Clearing | F.13 |
| 6 | Cusomer Reversal | |
| 6.1 | Reset Cleared Items | FBRA |
| 6.2 | Cusomer Document Reversal | FB08 |
| 6.3 | Mass Document Reversal | F.80 |
| 7 | Customer Account Display | |
| 7.1 | Customer Balance Display | FD10N |
| 7.2 | Display Customer Line Items | FBL5N |
| 7.3 | Display Customer Posting Document | FB03 |
Asset Accounting:
Asset Accounting Process:
| No | Asset Account Process |
| 1 | Asset Master Data |
| 2 | Asset Acquisition |
| 3 | Transfer of a fixed asset within company code |
| 4 | Sale of a fixed asset |
| 5 | Asset Retirement |
| 6 | Scrapping of a fixed asset |
| 7 | Depreciation posting |
| 8 | Depreciation Run Execution |
| 9 | Asset Report |
Asset Accounting Transaction:
No | Asset Transaction | T-Code |
| 1 | Asset Master Data | |
| 1.1 | Create asset master record | AS01 |
| 1.2 | Change asset master record | AS02 |
| 1.3 | Display asset master record | AS03 |
| 2 | Asset Acquisition | |
| 2.1 | Asset Acquisition with Vendor | F-90 |
| 2.2 | Asset Explorer | AW01N |
| 2.3 | Asset Report | S_ALR_87011965 |
| 2.4 | Depreciation Run | AFAB |
| 2.5 | Asset Transfer | ABUMN |
| 3 | Asset Retirement | |
| 3.1 | Asset Sale with Customer | F-92 |
| 3.2 | Asset Sale without customer | ABAON |
| 3.3 | Asset Retirement by Scrapping | ABAVN |
| 3.4 | Asset Retirement by Bulk Scrapping/Asset Balance | AR01 |
| 4 | Asset Explorer | AW01N |
| 5 | Depreciation Run Execution | AFAB |
5.Bank Accounting:
Bank Accounting Process:
| No | Bank Account Process | |
| 1 | Bank Master Data | |
| 2 | Check Management | |
| 3 | Create Check | |
| 4 | Display Check Information | |
| 5 | Void Check | |
| 6 | Cash Journal (Petty Cash Transactions) |
Bank Accounting Transaction:
| No | Bank Transaction | T Code |
| 1 | Create Bank Master Data | |
| 1.1 | Creation of Bank Keys | FI01 |
| 1.2 | Display Bank Master Data | FI03 |
| 1.3 | Change Bank Master Data | FI02 |
| 2 | Check Management | |
| 2.1 | Create Check Lots | FCHI |
| 2.2 | Change Check Lots | FCHI |
| 2.3 | Display Check Lots | FCHI |
| 2.4 | Create Check Information/Issue of Check | FCH5 |
| 3 | Display Check Information | |
| 3.1 | Display Payment Document | FCH2 |
| 3.2 | Check Register (Action taken) | FCHN |
| 3.3 | Change Check Information | FCH6 |
| 3.4 | Display Check Information | FCH1 |
| 4 | Void Check | |
| 4.1 | Check Void (Without Payment Reversal) | FCH9 |
| 4.2 | Void Check Not Used | FCH3 |
| 4.3 | Check Void (With Payment Reversal) | FCH8 |
| 4.4 | Check Payment with Print out | F-18 |
| 5 | Cash Journal (Petty Cash Transactions) | |
| 5.1 | Recording a Cash Receipt | FBCJ |
| 5.2 | Enter an Expense Transaction | FBCJ |
| 5.3 | Reverse Cash Journal | FBCJ |
| 5.4 | Cash Journal Report | S_P6B_12000118 |
SOME IMPORTANT CONCEPT FOR END USER
What does an SAP FICO End User do daily?
- Posting invoice into the system
- Posting customer Collections entries
- Recoding collections from customers
- Creating Purchase Orders
- Creating Goods Receipts
- Raising tickets for errors
- Vendor Payment
- Depreciation Posting
- Periodic voucher posting
- Preparing Vendor ageing repost
- Preparing Customer ageing report
- General Ledger posting
Users’ responsibilities are different as per different SAP modules. For example, the Sales Order creation, outbound delivery, and Sales Invoice are the responsibility of Logistics end users. The collection from the customer is the Finance end user’s responsibility.
Is there any difference in responsibilities between End users of” SAP FICO” and” S/4HANA Finance”?
Technically No. There is no major difference in the roles of the SAP S/4HANA Finance (Simple Finance) End-User and SAP FICO End User. It is just that they both use different platforms to work.While the SAP Simple Finance End-User works on the HANA application, the FICO End User works on ECC. However, the basic roles and responsibilities are still the same.
SAP FICO End User Duties Vs. an SAP Consultant’s role
The SAP consultant’s role is to develop the system and make the necessary changes for the end users. Whereas an SAP FICO End User only uses the SAP system. So, SAP end-users use the final product for operating a different business process.
The connection between SAP FICO End-User and a FICO Consultant
Although an SAP FICO End-User works differently, they are still connected to SAP FICO consultants. They both works on a similar platform, i.e., SAP Application. Be it ECC or S/4HANA.The SAP FICO End-Users need the help of Support Consultants in their day-to-day work lives.
1.How do they coordinate with each other?
Suppose there is an error during the business transaction. Then the end-user will raise the ticket. This ticket is assigned to a Support SAP consultant to resolve the issue., While posting one expenditure voucher, the user wants a default cost center that should be assigned with GL Master. So that every time an End-User need not select the Document Center while posting the expenditure. Now, you can automate this to system configuration, which is the responsibility of an SAP FICO Consultant. Likewise, it is similar to SAP S/4HANA Finance End-Users and Consultants. Related: SAP FICO Vs. SAP S/4HANA Finance
2. Is it good to start a career as an SAP End-User?
Yes, starting your career in SAP FICO as an end-user is perfectly ok if you are a fresher. The end user role is your first step to becoming an SAP Finance consultant.You need to understand the following points:-
- Firstly, having experience as an SAP End-user helps you to get the consultant job faster.
- Secondly, you are already familiar with the SAP system application. Thus it makes you adapt to the SAP environment easily.
- Third, when you take consultant-level training in SAP Finance, this experience will surely help you.
- Fourth, being knowledgeable of the technology in advance will keep you ahead of the competition while looking for jobs.
Finally, you can add this domain experience to your CV, making your profile more desirable. Do remember that most companies hire experienced people in consultants' roles. For that, the End-user experience is the best career step.
3. Growth chart of an SAP FICO End-user – Towards the consultant’s path
First, understand that End-users do the basic data entries in the system. The Associate Consultants do backend configuration/development, and the Support consultants resolve the users’ issues.So, suppose you join an IT company after getting equipped with configuration knowledge. In that case, you may join there as an associate consultant. And get the implementation and support projects. Else you may become a support consultant by joining a core company. Further growth chart goes as similar to an SAP Consultant if you become one.
4. How much knowledge of SAP FICO or S4 HANA Finance is required for the End-Users
Prior knowledge of the concerned module helps you familiarize yourself with the system. It would also help you adapt to the SAP application faster and more easily. Thus, it is always a good decision to learn SAP S/4HANA Finance or FICO beforehand.However, an end-user generally does basic general entries into the SAP system. Such as posting an invoice, collections, Purchase orders, Goods receipts, etc. To do this work, they generally get basic training in their company, where they join as end-user. An SAP support consultant or a senior in the team does this job. But they usually limit the level of knowledge to the requirement of data entry. However, many companies now prefer candidates with prior knowledge of accounting processes such as P2P and O2C and familiarity with the SAP ERP system. This clearly shows they expect you to have a bit of know-how of the SAP system. Thus, prior training in FICO or S/4HANA Finance will help you achieve your long-term goal of becoming a consultant
5. Is prior knowledge and experience required to get a job as an SAP FICO End User?
Experience is not required as such. But yes, as mentioned above, a decent amount of prior knowledge would help you get a better job faster. This will also help you to perform well on the job. However, since many companies hire complete freshers also end-users' roles, you may try finding such jobs and can apply for them as a beginner.
What kind of knowledge is good to have for SAP FICO end users?
Knowledge depends on the module you choose. In a Finance or SAP FICO End User’s role, you do Vendor payment, depreciation posting, periodical voucher posting, etc. So, a prior knowledge of Accounts, Finance, and SAP FICO is best. It will be an added advantage if you have learned SAP FICO basics. Many types of user profiles are available, such as Logistics, HR, ABAP, etc., other than Finance. Each module’s end-users are also different., The Logistics end-users or Data entry users create purchased orders, Goods Received, vendor invoices, Etc.
There are Super Users or Power Users, too, above End Users.
Super Users or power users have more rights to master data access and opening closing of posting periods. Thus, a company generally prefers to hire people with prior knowledge and experience in these positions. Read Related: Closing Activities in SAP S4 HANA Finance
6. How much is the demand for an SAP Finance End-User in the job market?
There is a huge demand for SAP End Users in the job market, mainly in Finance. Almost more than 70% of companies now work on SAP applications. They need End-Users in huge numbers. Thus, the job market is the best in SAP and keeps growing. You can say that the future in the SAP sector is really good, even in the End-user role. Since End-users are the entry-level staff, who feed the data into the system for business processing, they are in bulk demand.
7. What kind of industries hire SAP End Users?
Any core company that manufactures goods (SAP enabled) or any service company that works outsourced work (ITES industries) hires the End-user profile staff. You can look them up for vacancies on job sites. Else you can directly apply to their hiring box as and when they post them. These companies are good in numbers, thanks to the growing demand for SAP software.
8. How long should I work as SAP FICO End-user before applying for a consultant’s role?
If you aim to become an SAP consultant, in the long run, you should work up to 1.5 to 2 years to gain decent experience. In the meantime, don’t forget to learn SAP S/4HANA Finance configuration. You are already in the environment. So, the learning will have its best. Companies that are hiring for consultant roles prefer experienced candidates. So, after 2 years, you should start working towards future job roles. These are consultants, super users, Sr. Executives, Managers, etc. To conclude, a maximum of 2 years of experience is ok to stay in the role of an End-user before you choose to become an SAP FICO or S/4HANA Finance consultant.
Conclusion:
And then your aim is to become an SAP consultant in the long run, so go ahead gradually. There is a good demand for good SAP S4 HANA Finance consultants. So, strive to gain as much knowledge as possible being an end-user. Try to understand the SAP system well. Get in touch with the support consultants and keep analyzing their work methodology. Your interest in the system and your work will surely be observed by management. Then most importantly, don’t stop your studies. Continue learning SAP side by side. This way, when the right opportunity comes your way, you will be fully ready to grab it. Either in the same company or somewhere outside. I hope I have answered many questions of SAP Finance aspirants on how to start a career in SAP S/4HANA Finance smoothly. All the best.



